SOP
Go back to BioCompute Objects.
BCO Curation SOP
Intended audience: authors and developers
The following recommendations are intended to provide guidance on BCO™ creation, versioning, certification, and authentication.
BCO IDs and Versioning
Intended Audience: BCO authors
- BioCompute IDs are used as persistent URLs. A novel usability domain must result in the creation of a new BCO with a new BCO ID. BCO IDs are immutable upon creation and are never deleted or retired. If the usability domain (UD) remains unchanged, this results in a new version of the BCO. BCO ID example: OMX_000001
- BCO major and minor versions can be incremented based on project/institution documented policies.
- The BioCompute consortium maintains a database of registered authorities. Registered authorities are able to assign their reserved prefixes to their own IDs in the object_id field, such as OMX_000001. We encourage everyone to register a prefix at biocomputeobject.org.
BioCompute Certification(s) and Authentication
Intended Audience: commercial or academic entities looking for additional BCO support
Platform certification: A BioCompute “audit” will be conducted by the BioCompute Consortium. Requirements include:
- IEEE-2791 conformant BCOs can be created
- Security (ex: immutable upon creation, secure sharing, platform security)
- Data QC processes on input/output
Syntactical certification: Code is available on GitHub for download and use to ensure standard compliance.
Scientific certification: BCO consortium members will participate in the certification process; each certification process is projected to take ~ 3 months to 1 year to develop pipelines. Verification Kit: Input+output file(s) (in-silico generated), and Template BCO (tBCO) that includes error domain).
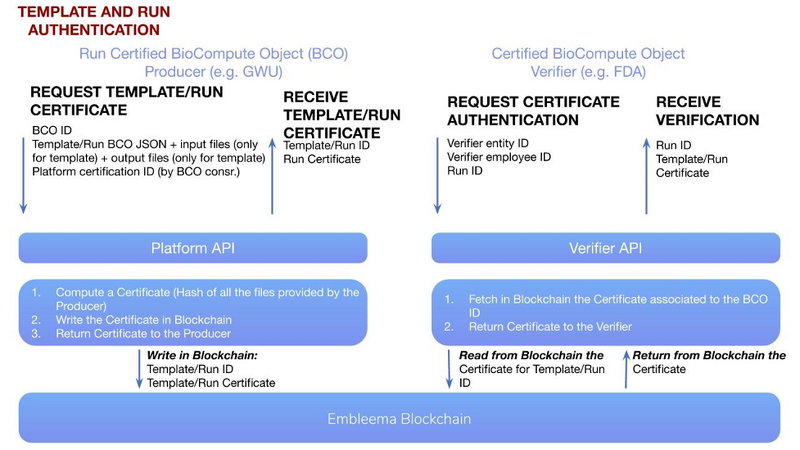
Template and Run Authentication: The Template BCO (tBCO) is created once along with a Verification Kit. Verification Kit usually includes in silico generated input files, BCO (with error domain) and output files. Run BCOs (rBCO) uses the tBCOs, and the only changes allowed are in the input (excluding reference files/databases) and output files field. tBCOs and rBCOs can be authenticated using secure blockchain technology.
- Template certification requirements: Input + output files
- Run certification requirements: certified template + run BCO (to confirm that parameters and error domain is within range etc.)
BCO Metadata
The three metadata fields are filled out at the time of submission. Validity check fills in the spec_version with the IEEE URL, an option to run a SHA256 (or just input your own hash value) for etag, and object_id is assigned (with the option to choose from any prefix associated with the account).
Domain-specific guidance
Execution domain
When recording manual curation, the script field of the execution_domain should link to a Google Document or GitHub markdown that describes the steps, either programmatically or in a stepwise fashion. Manual curation steps should ALSO be properly documented in the description_domain. An easy way to conceptualize this is: Description domain is for people, Execution domain is for machine (or programmers).
Extension domain
Format of how the schema would be defined: Execution domain
Error domain
This domain can support a “QA/QC rules” subdomain which provides rules that, if the output file does not pass the appropriate criteria, then it is flagged as an error.
BCO Form-based portal
Intended Audience: BCO tool developers and authors
BCOs can be created using any bioinformatics platform that has BCO read and writes functionalities. For users who do not have access to a bioinformatics platform they can use the BCO Builder in the BCO Portal which has some of the basic API functionalities:
- Create a BCO that is conformant to IEEE-2791.
- Download and install an instance within an organization’s firewall
- View videos and documentation on tool use
Versioning
Any version previous to the current version of a BCO is considered immutable and should not be edited. For example: Once an analysis has been recorded as a BCO, and has undergone several versioning changes, v1.0 of that BCO cannot be edited.
This documentation is currently in the commenting phase until Sept. 15, 2020. Please send your comments to Jonathon Keeney.